1.redis集群模式配置
1.引入redis的依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>redis.clients</groupId>
<artifactId>jedis</artifactId>
<version>3.7.1</version>
</dependency>
2.配置Jedis Pool和Client
# 最大连接数
spring.redis.pool.max-active=100
# 最大阻塞等待时间
spring.redis.pool.max-wait=2000
# 最大空闲连接
spring.redis.pool.max-idle=500
# 最小空闲连接
spring.redis.pool.min-idle=0
# redis的cluster实例配置
spring.redis.cluster.nodes={ip}:9000,{ip}:9001
# 执行命令超时等待时间
spring.redis.cluster.command-timeout=2000
3.定义属性对象
//定义redis pool集群的连接池 根据上述的配置进行映射
@Component
@Data
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "spring.redis.pool")
public class RedisClusterPool {
private int maxActive;
private int maxWait;
private int maxIdle;
private int minIdle;
}
//定义redis client集群节点实例
@Data
@Component
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "spring.redis.cluster")
public class RedisClusterProperties {
String nodes;
int commandTimeout;
}
4.定义redis cluster的配置类
@Configuration
@Slf4j
public class RedisClusterConfig {
@Autowired
private RedisClusterPool redisClusterPool;
@Autowired
private RedisClusterProperties redisClusterProperties;
//将jedis连接工厂注入到StringRedisTemplate中 如果不设置就使用默认的
@Bean(name = "redisTemplate")
public StringRedisTemplate redisTemplate(){
StringRedisTemplate stringRedisTemplate = new StringRedisTemplate();
stringRedisTemplate.setConnectionFactory(jedisConnectionFactory());
return stringRedisTemplate;
}
@Bean
public JedisConnectionFactory jedisConnectionFactory() {
//解析配置中的nodes
String[] nodes = redisClusterProperties.getNodes().split(",");
//将这些nodes生成到RedisClusterConfiguration中
RedisClusterConfiguration configuration = new RedisClusterConfiguration(Arrays.stream(nodes).toList());
//将RedisClusterConfiguration放入到连接池工厂中,加载时可以获取所有的节点
JedisConnectionFactory jedisConnectionFactory = new JedisConnectionFactory(configuration);
//将JedisPoo放入连接池工厂中,到时候生成JedisPool时就根据这些信息来生成
jedisConnectionFactory.setPoolConfig(initJedisPool());
log.info("init jedisConnectionFactory");
return jedisConnectionFactory;
}
//初始化JedisPool
private JedisPoolConfig initJedisPool(){
JedisPoolConfig jedisPoolConfig = new JedisPoolConfig();
jedisPoolConfig.setMaxIdle(redisClusterPool.getMaxIdle()); // 最大空闲连接数, 默认8个
jedisPoolConfig.setMaxTotal(redisClusterPool.getMaxActive()); // 最大连接数, 默认8个
jedisPoolConfig.setMinIdle(redisClusterPool.getMinIdle()); // 最小空闲连接数, 默认0
jedisPoolConfig.setMaxWaitMillis(redisClusterPool.getMaxWait()); // 获取连接时的最大等待毫秒数(如果设置为阻塞时BlockWhenExhausted),如果超时就抛异常, 小于零:阻塞不确定的时间, 默认-1
jedisPoolConfig.setTestOnBorrow(true); // 对拿到的connection进行validateObject校验
return jedisPoolConfig;
}
完成上述的配置,可以对SpringBoot的项目进行启动了。
2.Redis集群的启动原理
JedisConnectionFactory在afterProperties方法中需要创建JedisCluster对象,主要是为了加载JedisCluster的信息。
protected JedisCluster createCluster(RedisClusterConfiguration clusterConfig,
GenericObjectPoolConfig<Jedis> poolConfig) {
Assert.notNull(clusterConfig, "Cluster configuration must not be null!");
Set<HostAndPort> hostAndPort = new HashSet<>();
for (RedisNode node : clusterConfig.getClusterNodes()) {
hostAndPort.add(new HostAndPort(node.getHost(), node.getPort()));
}
int redirects = clusterConfig.getMaxRedirects() != null ? clusterConfig.getMaxRedirects() : 5;
return new JedisCluster(hostAndPort, this.clientConfig, redirects, poolConfig);
}
在创建JedisCluster的过程中会初始化slot cache,说到这个cache那就必须得说明下面的两个map
//nodes的映射关系是节点和对应的JedisPool key:ip:port作为key
private final Map<String, JedisPool> nodes = new HashMap<>();
//slots的映射关系是槽位和对应的JedisPool
private final Map<Integer, JedisPool> slots = new HashMap<>();
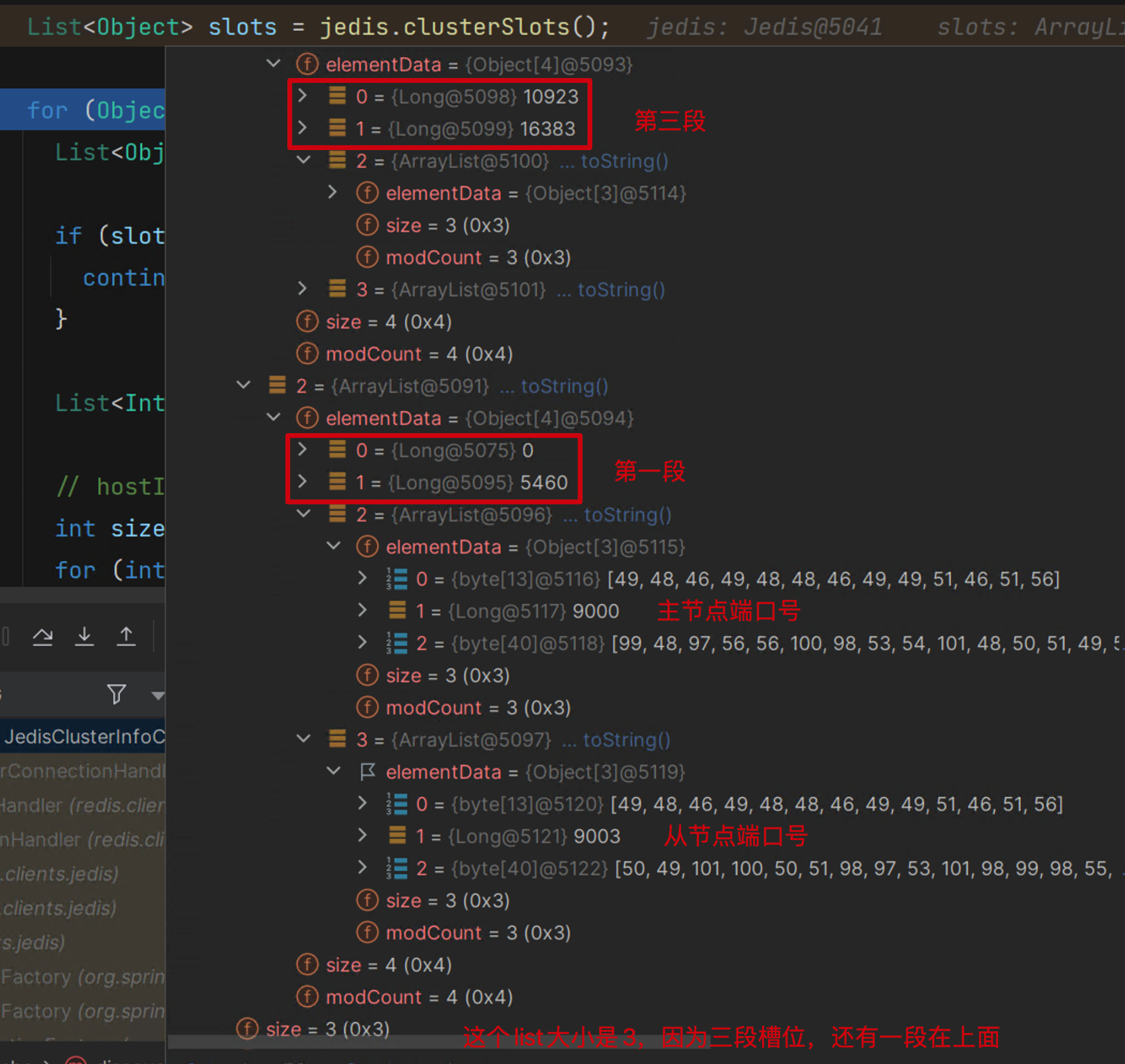
Note:nodes先完成加载,然后在加载slots时,根据ip和port构建出key,再根据key在nodes中取JedisPool放到slots中。如果是3个实例的话nodes的大小为三,不算从节点,但是对于slots中始终是16384,其中JedisPool是重用的。
redis.clients.jedis.JedisClusterInfoCache#discoverClusterNodesAndSlots
public void discoverClusterNodesAndSlots(Jedis jedis) {
w.lock();
try {
//重置redisPool 相当于归0操作
reset();
//模拟调用cluster slots命令 获取slots的数据
List<Object> slots = jedis.clusterSlots();
//
for (Object slotInfoObj : slots) {
List<Object> slotInfo = (List<Object>) slotInfoObj;
// <= 2时跳过后续的逻辑 该数据对象包含了:1.槽位起始;2槽位的结束;3.主节点(ip,实例id,端口号);4从节点 下述有截图
if (slotInfo.size() <= MASTER_NODE_INDEX) {
continue;
}
//根据槽位的起始和结束位置 构建一个list,list中是[21,22,23....4544,4555]这种
List<Integer> slotNums = getAssignedSlotArray(slotInfo);
// hostInfos
int size = slotInfo.size();
//从index=2开始 因为0和1位置都是槽位数据
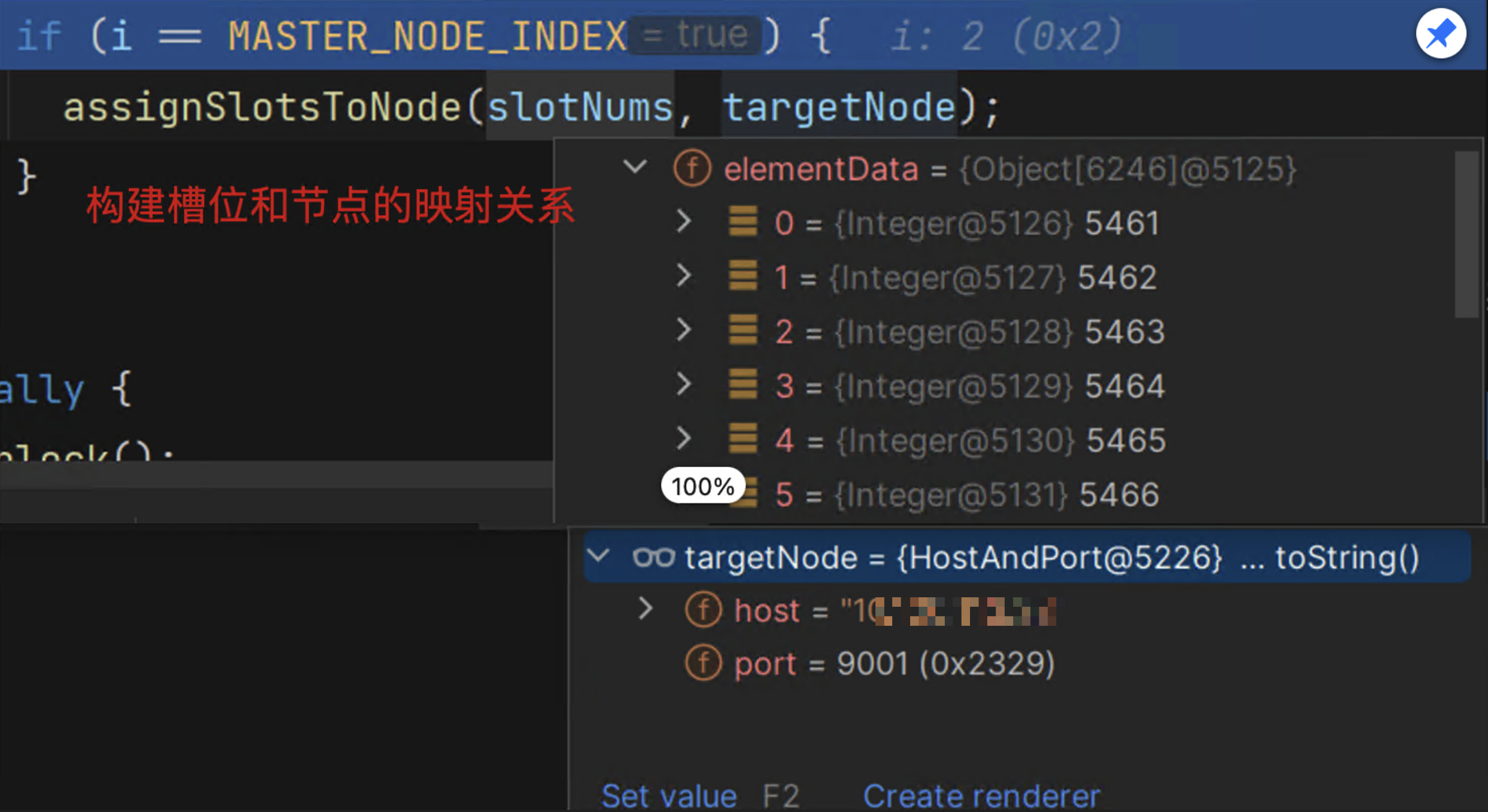
for (int i = MASTER_NODE_INDEX; i < size; i++) {
//获取节点数据
List<Object> hostInfos = (List<Object>) slotInfo.get(i);
if (hostInfos.isEmpty()) {
continue;
}
//节点对象转成含有ip和port的对象
HostAndPort targetNode = generateHostAndPort(hostInfos);
setupNodeIfNotExist(targetNode);
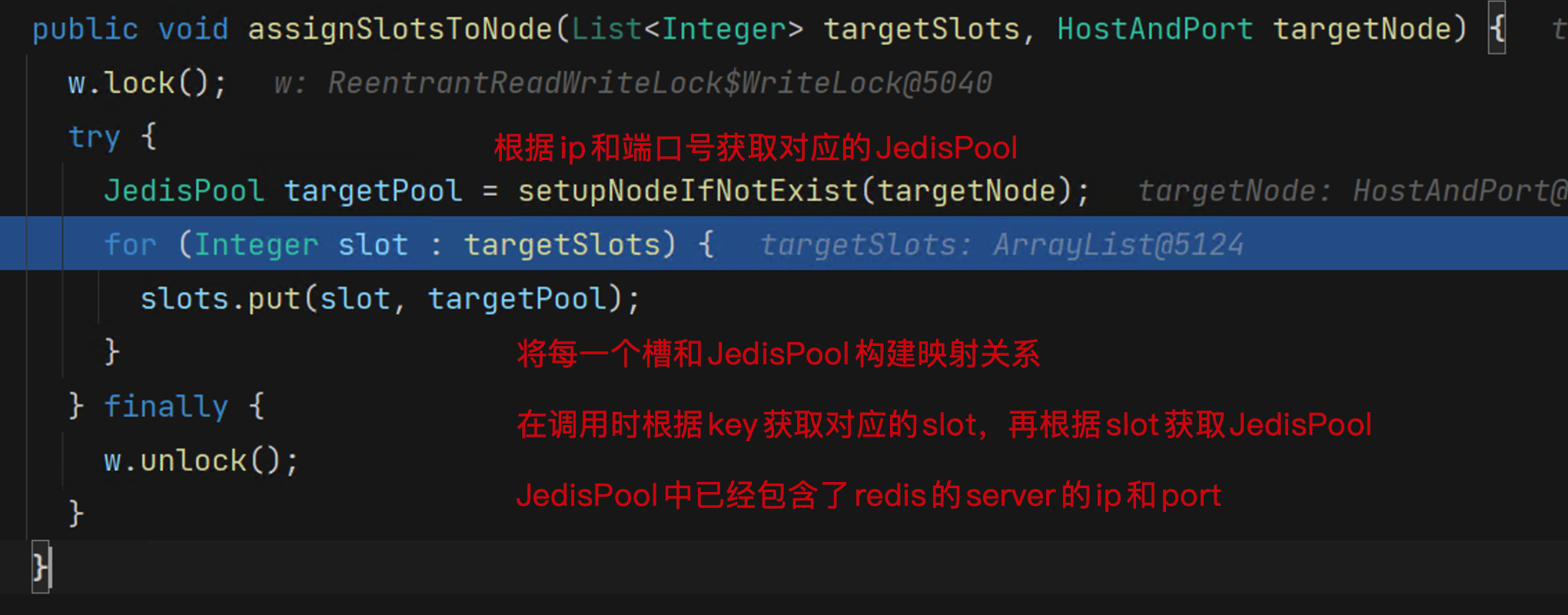
//当节点是主节点是,对其构建slot和jedisPool的映射关系
if (i == MASTER_NODE_INDEX) {
assignSlotsToNode(slotNums, targetNode);
}
}
}
} finally {
w.unlock();
}
}
redis.clients.jedis.JedisClusterInfoCache#setupNodeIfNotExist
//根据node生成JedisPool后放在cache里面
public JedisPool setupNodeIfNotExist(final HostAndPort node) {
w.lock();
try {
//nodeKey是{ip}:{port}形式
String nodeKey = getNodeKey(node);
//下面的逻辑时如果没有就创建 如果存在就返回
JedisPool existingPool = nodes.get(nodeKey);
if (existingPool != null) return existingPool;
JedisPool nodePool = new JedisPool(poolConfig, node, clientConfig);
nodes.put(nodeKey, nodePool);
return nodePool;
} finally {
w.unlock();
}
}
3.Redis集群的执行过程
3.1 get调用
get是基于同步调用的方式实现
redis.clients.jedis.BinaryJedisCluster#get
//调用get方法来获取数据
public byte[] get(final byte[] key) {
//采用匿名内部类的方式来实现方法的回调
return new JedisClusterCommand<byte[]>(connectionHandler, maxAttempts, maxTotalRetriesDuration) {
//等到执行runBinary后获取的连接后再去执行下述的get方法
@Override
public byte[] execute(Jedis connection) {
return connection.get(key);
}
//此处的方法实际上调用的是runWithRetries方法,该方法如下
}.runBinary(key);
}
redis.clients.jedis.JedisClusterCommand#runWithRetries
private T runWithRetries(final int slot) {
......
for (int attemptsLeft = this.maxAttempts; attemptsLeft > 0; attemptsLeft--) {
Jedis connection = null;
try {
if (redirect != null) {
connection = connectionHandler.getConnectionFromNode(redirect.getTargetNode());
//该异常是发生在扩容中
if (redirect instanceof JedisAskDataException) {
connection.asking();
}
} else {
connection = connectionHandler.getConnectionFromSlot(slot);
}
//根据获取的连接执行上述匿名内部类中定义的方法
return execute(connection);
} catch (JedisNoReachableClusterNodeException jnrcne) {
throw jnrcne;
} catch (JedisConnectionException jce) {
......
} catch (JedisRedirectionException jre) {
......
//如果是Moved的异常 会重新刷新本地的slot cache值
//这种一般是发生在扩容后 槽位发生了改变
if (jre instanceof JedisMovedDataException) {
// it rebuilds cluster's slot cache recommended by Redis cluster specification
//该操作和项目在启动时的行为一样 获取远程服务的cluster数据
this.connectionHandler.renewSlotCache(connection);
}
} finally {
releaseConnection(connection);
}
if (Instant.now().isAfter(deadline)) {
throw new JedisClusterOperationException("Cluster retry deadline exceeded.");
}
}
Note:
上述你会发现有两个异常: JedisAskDataException和JedisMovedDataException
两者区别:发生ASK重定向异常时,slot正在迁移,并未完成,该slot的一部分key在目标节点,一部分又在原节点,无法准确地将slot 与某个节点绑定,所以不会更新缓存,等到迁移结束后,用旧的缓存去请求key时,这时就会接收到redis返回的MOVED重定向异常,那会 才会更新缓存,维持缓存数据的准确性。
在扩容后,槽位发生改变,这时发生Moved Error,如下图所示:
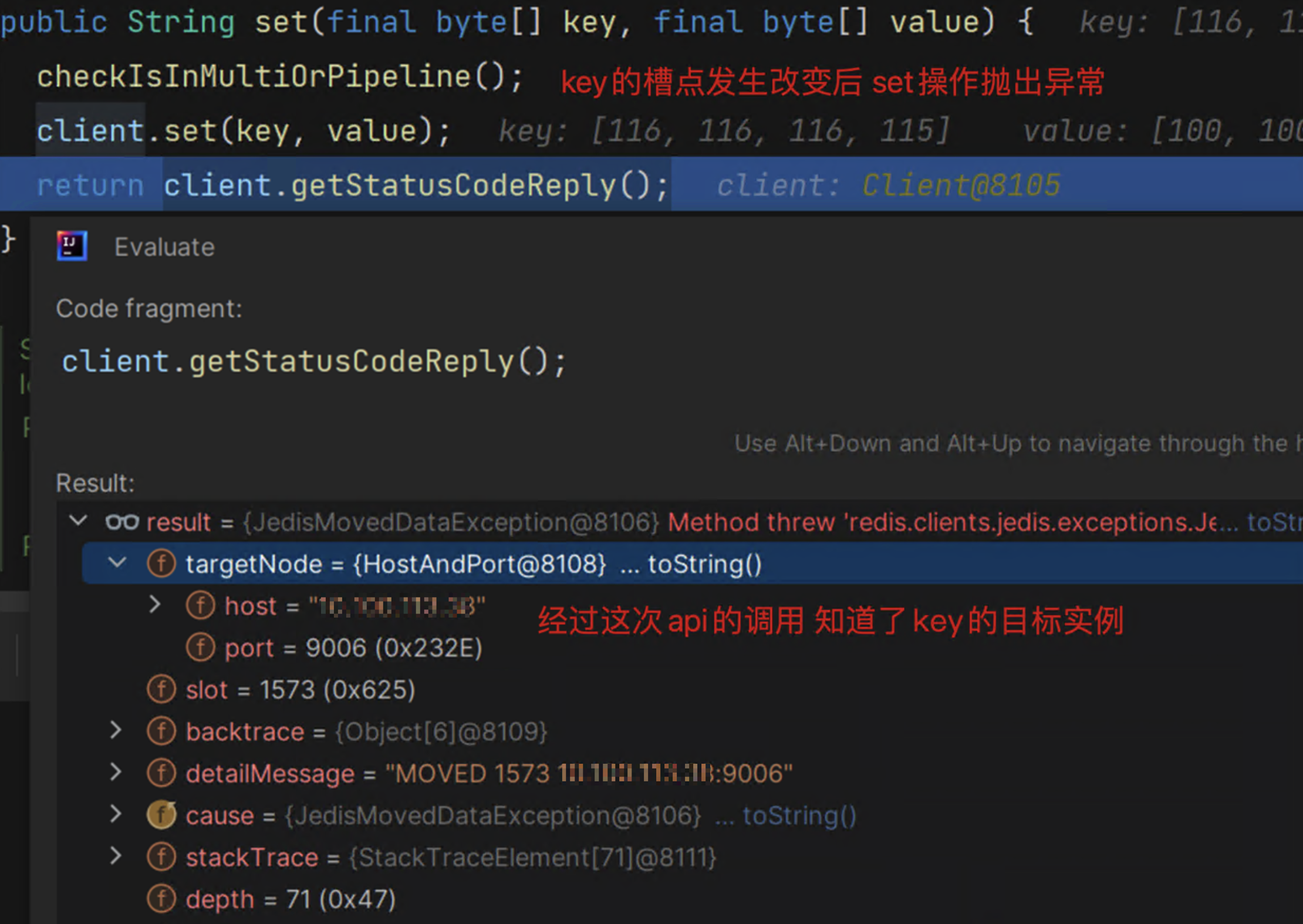
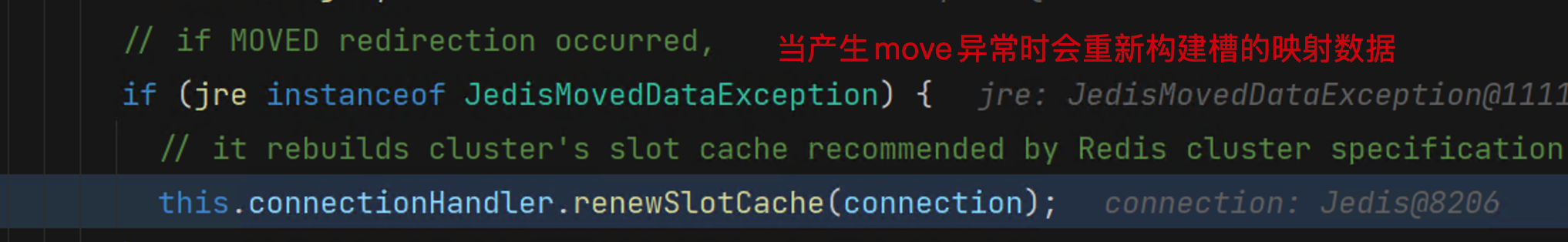
redis支持扩容是slot的变更,但是对于缩容时会产生问题CLUSTERDOWN Hash slot not served,这时候只能重启服务了。
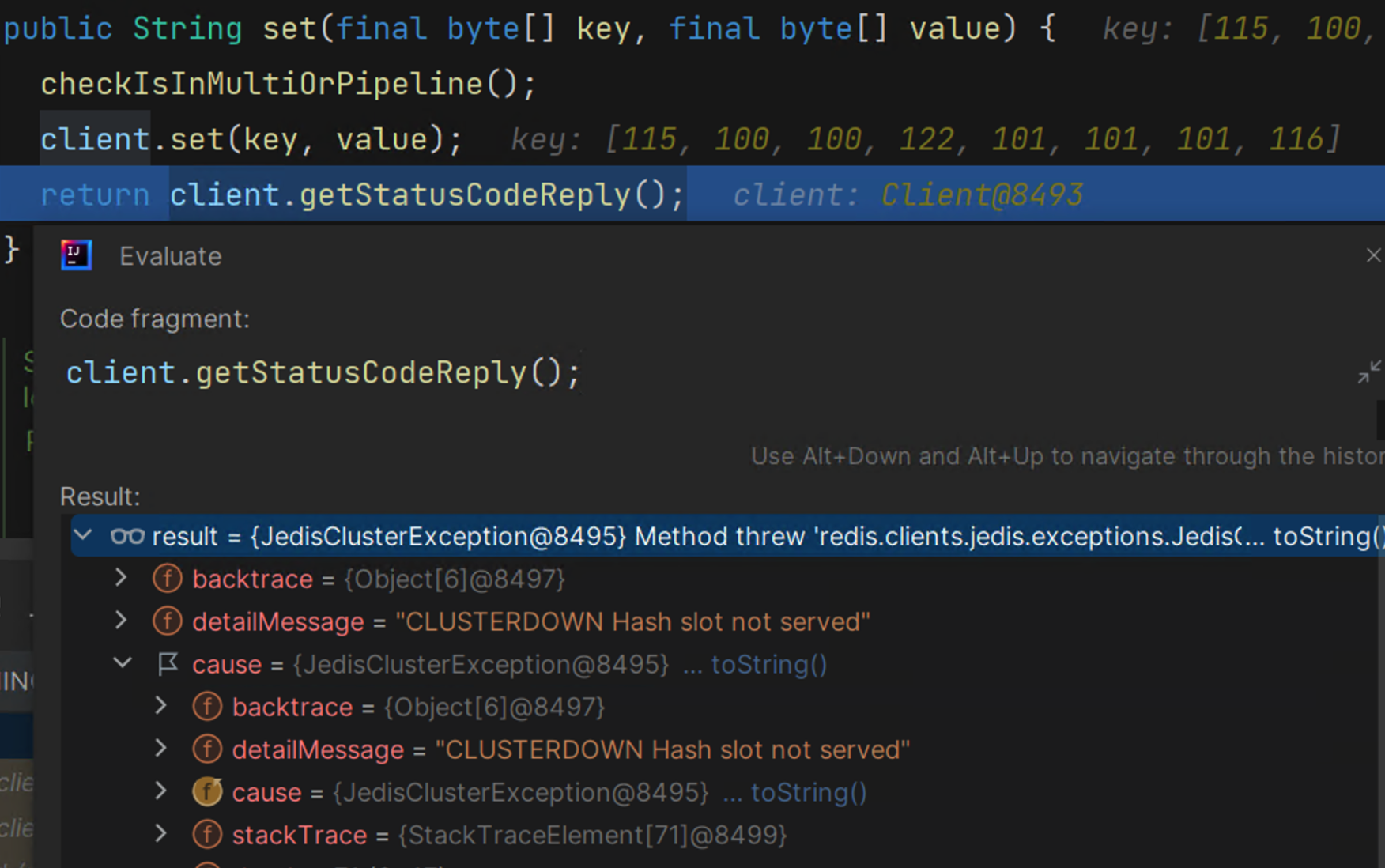
最后提供一张redis的执行流程图(图片来源于网络)
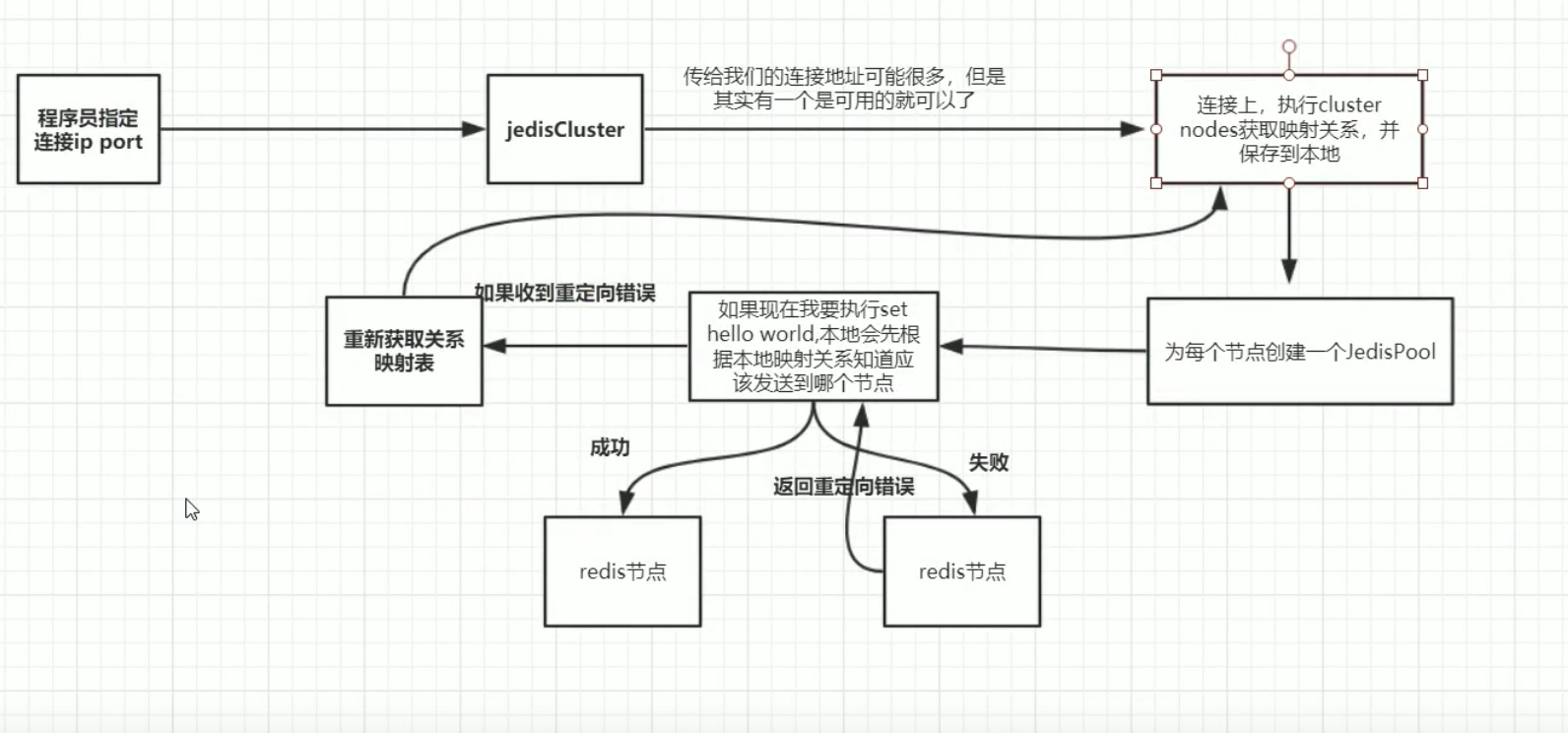
3.2 multiGet调用
mGet是可以批量的获取数据,和get区别的是使用了并行的方式,本质还是通过单个get任务扔到线程池中并行获取。
Note:multiGet对于没有获取到的数据会返回null值,业务中做好过滤null值。通常意义而已List中是不允许null值的,包括mybaits返回的List没有就不返回也不会在List中塞入null
public <S, T> MultiNodeResult<T> executeMultiKeyCommand(MultiKeyClusterCommandCallback<S, T> cmd,
Iterable<byte[]> keys) {
// //对所有的key根据节点进行分组
Map<RedisClusterNode, PositionalKeys> nodeKeyMap = new HashMap<>();
int index = 0;
for (byte[] key : keys) {
for (RedisClusterNode node : getClusterTopology().getKeyServingNodes(key)) {
nodeKeyMap.computeIfAbsent(node, val -> PositionalKeys.empty()).append(PositionalKey.of(key, index++));
}
}
//构建节点和根据key获取值任务的映射关系 后续需要根据future来获取结果
Map<NodeExecution, Future<NodeResult<T>>> futures = new LinkedHashMap<>();
for (Entry<RedisClusterNode, PositionalKeys> entry : nodeKeyMap.entrySet()) {
//要求去主节点获取数据
if (entry.getKey().isMaster()) {
//将该节点中的获取多个key的任务拆成一个个单一的任务扔到线程池中执行
//此处通过for循环的方式对一个个key扔到线程池中执行
for (PositionalKey key : entry.getValue()) {
futures.put(new NodeExecution(entry.getKey(), key),
executor.submit(() -> executeMultiKeyCommandOnSingleNode(cmd, entry.getKey(), key.getBytes())));
}
}
}
return collectResults(futures);
}
小编想法:不知道作者是出于什么原因,要把每一个key作为一个任务去获取,实际上把同一个节点的所有key放在一起批量获取即可。例如:可以先将所有的key按照节点进行分组,比如A节点就可以一把获取数据了,这样请求的次数从key的个数降到了小于等于节点数量。
后来做了一个实验:在同一个节点上使用mget时,即使这些key属于同一个节点,但是你会得到(error) CROSSSLOT Keys in request don't hash to the same slot的错误。这也就意味着redis只支持同一个slot情况下的批量获取,不支持同一个实例下的key批量获取。
4. 总结
本文主要讲述了redis的cluster集群模式的配置方式、启动加载cluster数据的原理、执行get和multiGet方法的原理。在扩容时发生槽位变更后,本地缓存会根据异常做出更新本地缓存的操作,但是对于缩容时是无法实现的。因为缩容后对应的server从集群中被移除,不提供服务了。
最后讲述一下redis的cluster模式为啥使用16384个槽位,而不是65535或者其他的。
首先引用作者原话比较有权威:
The reason is:
-
Normal heartbeat packets carry the full configuration of a node, that can be replaced in an idempotent way with the old in order to update an old config. This means they contain the slots configuration for a node, in raw form, that uses 2k of space with16k slots, but would use a prohibitive 8k of space using 65k slots.
-
At the same time it is unlikely that Redis Cluster would scale to more than 1000 mater nodes because of other design tradeoffs.
So 16k was in the right range to ensure enough slots per master with a max of 1000 maters, but a small enough number to propagate the slot configuration as a raw bitmap easily. Note that in small clusters the bitmap would be hard to compress because when N is small the bitmap would have slots/N bits set that is a large percentage of bits set.
结合作者原话,回答如下:
16384长度大小是2kb,65535大小为 8kb。由于每个节点之间互相存在心跳,该心跳主要用于同步节点的数据,例如有没有槽位的变更。如果节点太多,心跳的消息头太大了,占用带宽从而影响正常的业务;
作者建议不要使用超过1000个节点,节点太多会造成网络拥堵,那基于此前提的话,16384个槽完成够用了。确实够用,我在想作者是不是应该提供一个可配置的啊,比如我可能16384都用不到,我还想8192个槽位呢?或许你觉得我在抬杠,但是我个人认为对于这种阈值的解释很有主观因素。例如:为啥MySQL的页大小是16kb?为啥HashMap是0.75时扩容?为啥ArrayList初始容量是10?